and Contracting IT Outsourcing Contracts
STUDENT PAPER
By Sophie Malherbe
SKEMA Business School
Chambourcy, France
ABSTRACT
An Information Technology subcontracting relationship can meet many issues, which can arise during the pre-contractual phase or the already-started business relationship. This fact shows that there is a strong important to choose adapted clauses and provisions when writing the contract and a key verification of all the details to do during the whole contracting process.
Then, the main objective of this paper is to give both parties, the IT supplier and the customer company, the key elements essential to protect their interests and their projects.
When willing to enter or entering into an IT outsourcing contract with an IT supplier, a customer company has to secure its contract from its negotiation, thanks to prevention and cooperation, to the signature of the agreement. On the other hand, if unfortunately a dispute arises after both parties entered into their legal IT relationship, it is recommended to them to have implemented the “Dispute Resolution” clause providing them to use the Standing Neutral alternative solution. This option generally makes the parties saving costs and time, beneficing of a neutral and very competent third party familiar with the contract’s environment (projects, relationship, privacy, etc.).
Keywords: Dispute, Contracts, Management, Solution, Information Technology, Outsourcing, Subcontracting, Negotiating
INTRODUCTION
Because of the acceleration of the digitalization of business processes, more and more companies all over the world start or already have projects of software development. These projects are generally part of development portfolios to make a company more competitive: it is a strategic key point (Figure 1[1]). “In response, the organization as a whole and its IT group in particular has to continuously evolve to be more agile and robust”[2].
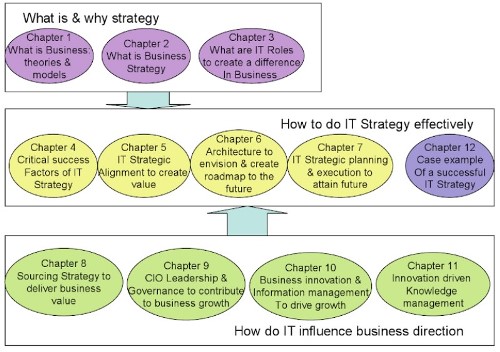
Figure 1: Why IT development and implementation within a company is strategic?[3]
To achieve this Digital Transformation, thanks to their software development, some companies, such as IBM, create their own software, use it personally and sell it to other companies. Otherwise, some other companies do Information Technology (IT) outsourcing which is “the subcontracting of a part of all of the IT function of a company to an external outsourcing vendor”[4].
Outsourcing has profoundly evolved over time. Now, more than being a way to externalize the production in order to minimize manufacturing costs thanks to third parties, it entails “several strategically important functions: from technological innovation to logistics, customer relations to post-sales services”[5].
More…
To read entire paper, click here
Editor’s note: Student papers are authored by graduate or undergraduate students based on coursework at accredited universities or training programs. This paper was prepared as a deliverable for the course “International Contract Management” facilitated by Dr Paul D. Giammalvo of PT Mitratata Citragraha, Jakarta, Indonesia as an Adjunct Professor under contract to SKEMA Business School for the program Master of Science in Project and Programme Management and Business Development. http://www.skema.edu/programmes/masters-of-science. For more information on this global program (Lille and Paris in France; Belo Horizonte in Brazil), contact Dr Paul Gardiner, Global Programme Director paul.gardiner@skema.edu.
How to cite this paper: Malherbe, S. (2019). Dispute Resolution when Negotiating and Contracting IT Outsourcing Contracts, PM World Journal, Vol. VIII, Issue VII, August. Available online at https://pmworldlibrary.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/pmwj84-Aug2019-Malherbe-dispute-resolution-for-IT-outsourcing-contracts.pdf
About the Author

Sophie Malherbe
Chambourcy, France
![]()
Sophie Malherbe is a Global Project Management professional with Law background. Born in the Human Rights’ country, France, she has a Dual Bachelor’s degree in French Law and Common Law from the University of Nanterre (Law School). During her study, in 2017, she had the opportunity to work as a Junior Project Manager at Vivatechnology, a joint-venture created by Maurice Levy (Publicis Group) and Francis Morel (Les Échos, LVMH). She trained herself for six months to become a great and efficient future Project Manager by participating in the organization of a worldwide meeting between startups, investors and big companies from around the whole globe.
She pursued her education by starting to study at SKEMA Business School (France) in 2017. Since she joined this 7th best-ranked French Business School, she already had the chance to enroll for a study semester in Belo Horizonte (SKEMA’s Brazilian campus in partnership with the Fundação Dom Cabral, being a world-class Brazilian business school). She now studies Global Project Management in the Master of Sciences “Project and Programme Management and Business Development” at SKEMA Business School (Lille campus France). She is actually completed her last assignments and took the opportunity to further her education by a way of a distance learning mentoring course, under the tutorage of Dr Paul D. Giammalvo, to obtain her International Contract Management degree.
Sophie lives in Chambourcy, France and can be contacted at sophie.malherbe@skema.edu.
To find other information about Sophie Malherbe, visit her LinkedIn profile at https://www.linkedin.com/in/sophie-malherbe-skemabusinessschool-projectmanagement-it/
[1] “Information Technology Strategy and Management: Best Practices” – Chew, Eng K – Retrieved from https://books.google.fr/books?id=oOYioSahlYgC&pg=PT330&lpg=PT330&dq=Strategies+for+dispute+prevention+and+management+in+IT+outsourcing+arrangements&source=bl&ots=oOcnF0Vn5d&sig=LDwL4TP6oeG8Dr7-trHUrK8pYWw&hl=fr&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjexdHfyNveAhUvzoUKHSiKCRA4ChDoATAFegQIBxAB#v=onepage&q&f=false
[2] “Information Technology Strategy and Management: Best Practices” – Chew, Eng K – Retrieved from https://books.google.fr/books?id=oOYioSahlYgC&pg=PT330&lpg=PT330&dq=Strategies+for+dispute+prevention+and+management+in+IT+outsourcing+arrangements&source=bl&ots=oOcnF0Vn5d&sig=LDwL4TP6oeG8Dr7-trHUrK8pYWw&hl=fr&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjexdHfyNveAhUvzoUKHSiKCRA4ChDoATAFegQIBxAB#v=onepage&q&f=false
[3] “Information Technology Strategy and Management: Best Practices: Best Practices” – Chew, Eng K – Retrieved from https://books.google.fr/books?id=oOYioSahlYgC&pg=PT330&lpg=PT330&dq=Strategies+for+dispute+prevention+and+management+in+IT+outsourcing+arrangements&source=bl&ots=oOcnF0Vn5d&sig=LDwL4TP6oeG8Dr7-trHUrK8pYWw&hl=fr&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjexdHfyNveAhUvzoUKHSiKCRA4ChDoATAFegQIBxAB#v=onepage&q&f=false
[4] “Information systems outsourcing: issues and evidence” – K. Altinkemer, A. Chaturvedi, R. Gulati – Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0268401294900035
[5] “Outsourcing strategies. How to formalize and negotiate the outsourcing contract”, Pallicelli Michela and Meo-Colombo Carlotta – Retrieved from https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/6294468.pdf









