in an Indonesian Oil and Gas Company
FEATURED PAPER
By Yoga Putra Andrian
Jakarta, Indonesia
ABSTRACT
In the face of escalating global energy demands, the construction and management of pier infrastructure emerge as pivotal challenges, particularly for energy companies like Pertamina Patra Niaga in Indonesia. This paper aims to optimize pier construction management through the implementation of an OmniClass Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), addressing the critical need for standardized project management methodologies in complex, large-scale construction projects. By integrating a multidimensional WBS approach, akin to the hypercube or tesseract model, this study explores the enhancement of project planning, execution, and management. Employing a comprehensive literature review and case study analysis, the research investigates the efficacy of OmniClass WBS in facilitating better project coordination, cost estimation, and risk management. The findings underscore the significant advantages of adopting a standardized, multidimensional WBS, including improved data management and project outcome predictability. This paper concludes that the OmniClass WBS framework not only optimizes pier construction projects but also serves as a model for future infrastructure development endeavors within the energy sector
Keywords: WBS, Multi-Dimensional, Pier Construction, Project Management Classification, Best Practices, Building Information Modeling (BIM), Omniclass, MADM, ISO1908:2016, Coding Structure, Artificial Intellegence, Economtrics, Data Management, Data Engineering
INTRODUCTION
Global Energy Needs
Global energy needs are experiencing a significant increase, a phenomenon triggered by various population growth, economic expansion, and technological development. As the world’s population increases, especially in developing countries, there is a rising demand for energy for daily needs, ranging from lighting and heating to transportation. Rapid economic growth in many countries also burdens on energy resources, as industries and commercial sectors require more energy to support their operations and expansion. According to the International Energy Outlook 2017 (IEO2017) released by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), global energy consumption is projected to grow by 28% from 2015 to 2040[1]. This projection includes estimates of energy demand based on region and primary energy sources, power generation based on energy sources, and carbon dioxide emissions associated with energy.
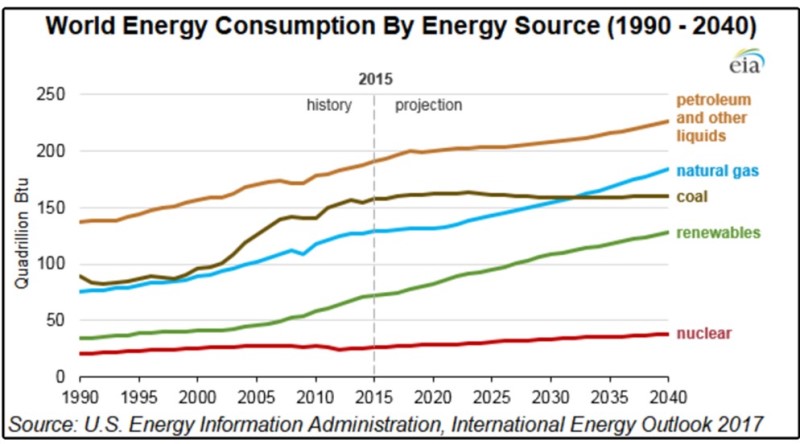
Figure 1 – World Energy Consumption [2]
This trend is also in line with the projected energy needs in Indonesia. According to a report from the Central Bureau of Statistics, by 2050, Indonesia’s energy needs are expected to reach 2.9 billion barrels of oil equivalent (BOE), an increase from the 2040 projection of 2.1 billion BOE. This increase is influenced by economic and population growth, energy prices, and government policies [3]. Sectorally, the industry is expected to be the largest energy consumer, with an average annual growth of about 3.9%. infrastructure in all corners of Indonesia to meet its obligations effectively. This commitment is made clear through the company’s annual town hall meetings, emphasizing expanding storage capacity.
Other sectors, such as commercial, household, and related sectors, will also experience an increase in energy needs in line with economic and population growth. However, the transportation sector is expected to have a lower growth rate than the industry, at about 3.2% per year.
More…
To read entire paper, click here
How to cite this paper: Andrian, Y. P. (2024). Building an Econometrics Model for Pier Construction in an Indonesian Oil and Gas Company; PM World Journal, Vol. XIII, Issue IV, April. Available online at https://pmworldlibrary.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmwj140-Apr2024-Andrian-building-an-econometrics-model-for-pier-construction.pdf
Editor’s note: This paper was originally prepared during a 6-month long Graduate-Level Competency Development/Capacity Building Program developed by PT Mitrata Citragraha and led by Dr. Paul D. Giammalvo to prepare candidates for AACE CCP or other Certifications. https://build-project-management-competency.com/our-faqs/
About the Author

Yoga Putra Andrian
Jakarta, Indonesia
![]()
Yoga Putra Andrian Yoga Putra Andrian is an engineer with nearly a decade of experience, working in Indonesia’s national oil and gas company. He has worked on various projects, including pier construction, pipeline installation, and fuel terminals. He holds a Bachelor’s degree in mechanical engineering from the Bandung Institute of Technology (ITB) and a Master of Business Administration from Gadjah Mada University (UGM). He is enrolled in a distance learning course led by Dr. Paul D. Giammalvo to obtain Certified Cost Professional certification from AACE International.
Yoga Putra Andrian resides in Jakarta, Indonesia, and his email address is yogandrian@gmail.com.
[1] Davis, C. (2017, September 14). Global NatGas Fastest Growing Fossil Fuel to 2040 as Supply, Trade Soars, Says EIA. Natural Gas Intelligence. Retreived from https://www.naturalgasintel.com/global-natgas-fastest-growing-fossil-fuel-to-2040-as-supply-trade-soars-says-eia/
[2] Davis, C. (2017, September 14). Global NatGas Fastest Growing Fossil Fuel to 2040 as Supply, Trade Soars, Says EIA. Natural Gas Intelligence. Retreived from https://www.naturalgasintel.com/global-natgas-fastest-growing-fossil-fuel-to-2040-as-supply-trade-soars-says-eia/
[3] Mutia, A. (2021, Desember 3). Kebutuhan Energi Indonesia Diproyeksikan Capai 2,9 Miliar Setara Barel Minyak pada 2050. Databoks Katadata. Retreived from: https://databoks.katadata.co.id/datapublish/2021/12/03/kebutuhan-energi-indonesia-diproyeksikan-capai-29-miliar-setara-barel-minyak-pada-2050









